Fertilizer granules
Fertilizer granules play a vital role in modern agriculture by providing a convenient and efficient way to deliver essential nutrients to plants. These small, compact particles contain concentrated nutrients and are designed to release their contents gradually, ensuring optimal nutrient uptake by plants.
Benefits of Fertilizer Granules:
Controlled Nutrient Release: Fertilizer granules are engineered to release nutrients slowly over time, providing a consistent supply to plants. This controlled-release mechanism helps prevent nutrient leaching, reduces the risk of nutrient runoff, and ensures that plants receive a steady and balanced nutrient supply, maximizing their growth potential.
Increased Nutrient Use Efficiency: The slow-release nature of fertilizer granules improves nutrient use efficiency. Nutrients are available to plants when needed, reducing the risk of over-fertilization and minimizing nutrient losses to the environment. This leads to improved crop yield, reduced input costs, and more sustainable agricultural practices.
Ease of Application: Fertilizer granules are easy to handle, store, and apply. Their uniform size and shape facilitate even distribution, ensuring consistent nutrient availability throughout the crop field. Granular fertilizers can be applied using various equipment, such as spreaders or seeders, allowing for efficient and precise nutrient placement.
Nutrient Customization: Fertilizer granules can be tailored to meet specific crop and soil nutrient requirements. By adjusting the composition and formulation of the granules, it is possible to create blends with specific nutrient ratios or add secondary and micronutrients as needed. This flexibility allows farmers to optimize nutrient applications based on crop demands and soil conditions.
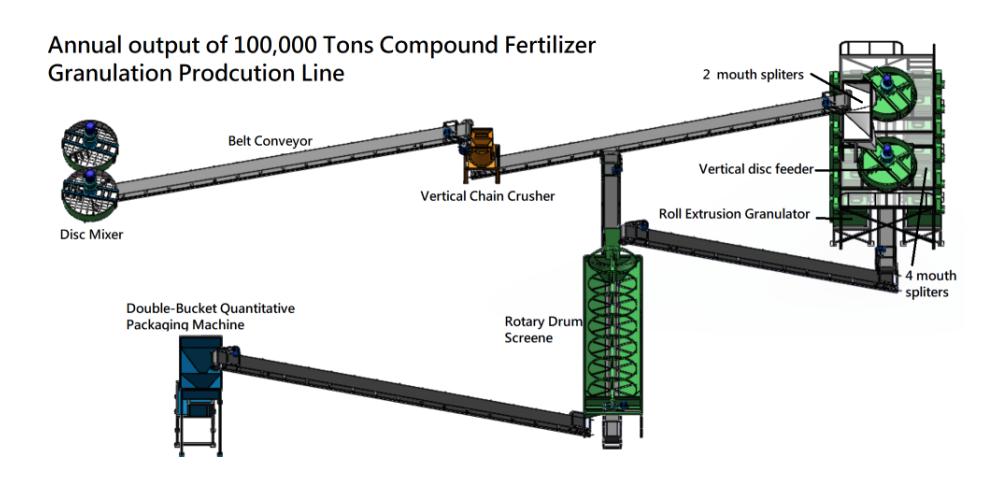
Production Process of Fertilizer Granules:
The production of fertilizer granules involves several key steps:
Formulation: The formulation process involves determining the nutrient composition and ratios needed for the specific crop and soil conditions. It considers factors such as the crop’s nutrient requirements, soil nutrient levels, and desired release characteristics.
Mixing: Once the formulation is established, the raw materials are mixed thoroughly to ensure a homogeneous blend. This step combines the base nutrients, secondary nutrients, micronutrients, and any additional components required for the specific fertilizer blend.
Granulation: The mixed fertilizer formulation is then transformed into granules. Granulation can be achieved through various methods, such as extrusion, compaction, or prilling. These processes involve applying pressure, heat, or binding agents to form the granules.
Drying and Cooling: After granulation, the newly formed fertilizer granules undergo a drying process to remove excess moisture. Subsequently, they are cooled to prevent clumping and ensure proper storage stability.
Applications of Fertilizer Granules:
Field Crops: Fertilizer granules are widely used in field crop production, including grains, oilseeds, and legumes. The slow-release nature of the granules provides a consistent nutrient supply throughout the growing season, supporting healthy plant growth, optimizing yield potential, and reducing environmental impact.
Horticulture and Specialty Crops: Fertilizer granules are beneficial for horticultural and specialty crops, such as fruits, vegetables, ornamentals, and turfgrass. The controlled-release of nutrients ensures steady growth and improved nutrient uptake, resulting in healthier plants, better quality produce, and enhanced aesthetic appeal.
Sustainable Agriculture: Fertilizer granules contribute to sustainable agricultural practices by minimizing nutrient losses and environmental impact. The controlled-release mechanism helps reduce the risk of nutrient runoff, leaching, and volatilization, promoting efficient nutrient use and minimizing adverse effects on water bodies and ecosystems.
Precision Agriculture: Fertilizer granules are compatible with precision agriculture technologies, enabling targeted nutrient applications based on site-specific needs. This approach allows farmers to apply the right amount of nutrients precisely where and when they are needed, maximizing nutrient use efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
Fertilizer granules offer numerous benefits, including controlled nutrient release, increased nutrient use efficiency, ease of application, and nutrient customization. The production process involves careful formulation, mixing, granulation, drying, and cooling to create high-quality granules. Fertilizer granules find applications in field crops, horticulture, specialty crops, sustainable agriculture, and precision agriculture.