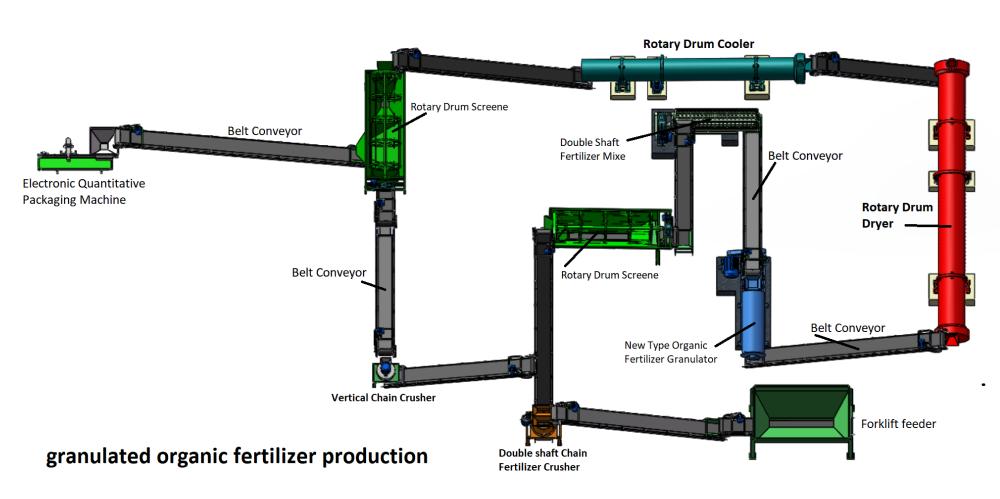
Compound fertilizer drying and cooling equipment
Compound fertilizer drying and cooling equipment are used in the final stage of the production process to remove excess moisture from the compound fertilizer and lower its temperature. This helps to improve the quality and stability of the fertilizer, as well as increase its shelf life.
There are several types of compound fertilizer drying and cooling equipment, including:
1.Rotary Dryer: A rotary dryer is a type of drying equipment that uses a rotating drum to dry the compound fertilizer. The drum is heated using gas, electricity, or steam, and the fertilizer is fed into the drum at one end and discharged at the other end. The hot air circulates through the drum, removing moisture from the fertilizer.
2.Fluidized Bed Dryer: A fluidized bed dryer is a type of drying equipment that uses hot air to fluidize and dry the compound fertilizer. The fertilizer is fed into a bed of hot air, which causes it to become suspended and fluidized. The hot air then removes the moisture from the fertilizer.
3.Belt Dryer: A belt dryer is a type of drying equipment that uses a conveyor belt to move the compound fertilizer through a heated chamber. The hot air circulates through the chamber, removing the moisture from the fertilizer as it passes through.
4.Drum Cooler: A drum cooler is a type of cooling equipment that uses a rotating drum to cool the compound fertilizer. The fertilizer is fed into the drum at one end and discharged at the other end, while cold air is circulated through the drum to cool the fertilizer.
5.Counter Flow Cooler: A counter flow cooler is a type of cooling equipment that uses a counter-flow principle to cool the compound fertilizer. The fertilizer is fed into the cooler at one end and discharged at the other end, while cold air is circulated in the opposite direction to cool the fertilizer.
When choosing the type of drying and cooling equipment for compound fertilizer production, it is important to consider factors such as the type and moisture content of the fertilizer, the desired end product, and the production capacity of the production line.